Model Documentation Examples
General Model Overview
The model is a pre-trained question-answering language model based on Google’s BERT language model and trained using the Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQUAD).
The model is further trained on a proprietary dataset of financial documents to improve its performance on finance related documents and questions.
Examples of questions and answers are:
Q: What is the total invoice value? A: $55,000
Q: What is the email of the author? A: john@gravity-futures.com
Q: When is this document dated? A: January 6th 2018.
The model is not a text classifier.
Business & Executive
Expected ROI / Savings
The primary benefits of the model are to reduce the need for manual reading and comprehension of documents.
A domain experienced person can be expected to read and answer questions at approximately 200 words a minute. Assuming an employee cost of $300 per hour, this is $5 per minute, and 40 words per dollar per minute.
A cautious estimate for machine question answering is 200,000 words per minute, with an operating cost of $0.1 per minute, and 2 million words per dollar per minute.
Assuming 5% of documents require human intervention this is a cost improvement.
In addition, human errors are far more inconsistent than model errors. This means model errors can be compensated for, or used to inform further model training.
Recommended Use Cases
Title:
Searching a document repository for invoices from a specific supplier.
Description:
The model can be asked to identify documents which have a specified supplier name located in the expected locations in the document, such as document headers, address fields and sign-off signatures.
Title:
Prioritising incoming application forms based on criteria contained within the documents.
Description:
The model can be used to select and order documents based on content which indicates priority. For example, documents containing indications of being “urgent” or a “final demand” can be prioritised above those indicating a “reminder”.
Business Fit
The model can be used to aid financial reconciliation processes by ensuring an automated search for invoice documents from a specific supplier match manual processes.
The model can be used to aid an audit of supplier spend by supporting the search of financial documents.
The model can be used to automatically identify those customers using a customer service chatbot who are particularly unhappy, frustrated or in a vulnerable state.
Anti Patterns
The model is not intended to take free-form queries directly from end-users, such as the public, as performance is diluted in this scenario. The range of queries should be constrained to be domain-specific, and their performance should be tested before use, and regularly during.
This customer sentiment analysis model should not be used to automate responses to customers identified as unhappy or in a vulnerable state. The alert should be escalated for a person.
Implementation & Governance
Model Architecture
Diagram
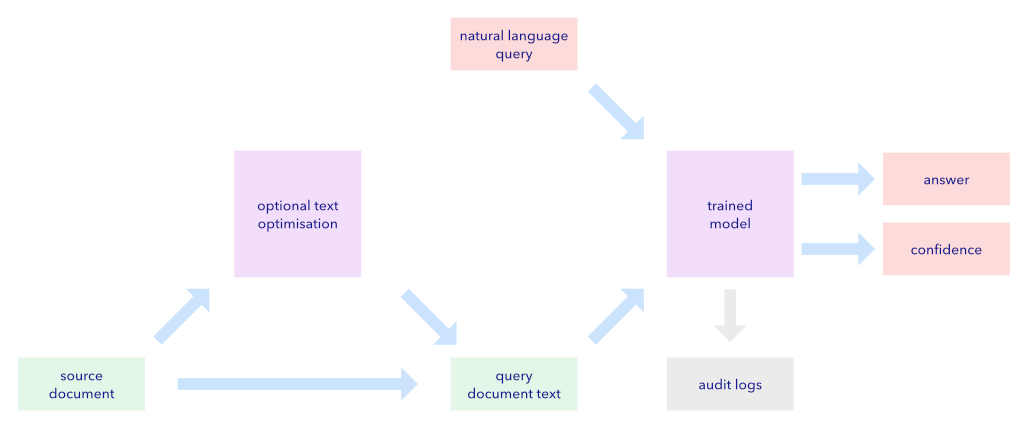
Description
The architecture overview presents the key elements of the model and data pipeline. There are two loosely-coupled elements - a question answering pre-trained model, and a preceding text extraction and optimisation engine.
The pretrained question answering model takes as input, a query document in the form of plain text, and a natural language query. Its output is the answer to the natural language question, together with a confidence score for that answer.
The query document text is prepared from source documents which are in PDF form. These PDFs are converted to images, and an OCR module converts these bitmaps to text. Optional text optimisation can be enabled to, for example, correct common misspellings or apply an organisational taxonomy.
Currently any text within source PDFs is not extracted.
The question answering model can optionally log all queries and answers for audit and diagnostics purposes.
Input Data
| Name | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Language Question | String 3-20 words. | This is the natural question issued to the model. |
| Age | Integer 18-130. | The age of the customer. Should not be below 18. |
Output Data
| Name | Format | Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Document IDs | String | The document identifiers matching the query. | The returned documents have a high likelihood of being relevant to the search query provided as input. Only 10 document IDs are returned, and these are ordered by relevance. If less than 10 returned, it is because there were not enough documents with a high enough matching score. |
| Grant Load | Boolean Yes/No | Indicates whether the customer is recommended to be granted a loan or not. | The information provided about the customer has been evaluated by the model as sufficient to indicate a good loan customer when compared to the evidence base of the training data. |
| Confidence | Number 0-100 | Confidence score for the model’s recommendation. | A score above 70% is very certain. A score 50-70% is to be interpreted as moderately conclusive. A score below 50% indicates insufficient information about the customer to make a conclusive decision either way. It is not an indication of a loan rejection. |
Explainability of Outputs
The decision tree supporting the model’s output can be extracted. Model outputs are readily interpretable in terms of the customer information provided as input.
Typically the customer’s age and average income are the most significant factors in a loan decision.
Performance
90%
The model achieves a correct identification rate of 90% when trained on the MNIST training data set using 20 training epochs and tested against the MNIST test dataset.
Further performance stability testing including ROC curves for tunable model parameters is at the provided URL.
http://www.test.com/performance.pdf
Training Data
Title:
MNIST dataset
Overview:
MNIST is an image dataset of handwritten digits, commonly used for training various image processing systems. The database contains 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images. Each digit is a 28x28 bitmap, with each pixel a grey-scale value 0-255.
Additional Processing:
The MNIST dataset has been augmented by taking each training image and rotating it ±5, ±10, ±20 degrees, effectively expanding the training data seven-fold. The aim is to provide additional training samples where characters are rotated a small amount , reflecting real world data.
URL:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MNIST_database
Hardware Requirements
CPU:
2 Cores
RAM:
16 GB
GPU: (optional)
8GB
Runtime:
A few minutes
Risk & Compliance
Blackbox Model
This is a blackbox model.
Privacy Risks
Training Data
The model is a general question answering system which returns information from a training database of financial documents from your organisation which can contain personal information, such as names, telephone numbers and addresses.
It is possible to apply, an albeit imperfect, filter to remove records containing personal information from this dataset, but this has an overall negative effect on the usefulness of the training data.
Risk to Individuals
To control the risk of unauthorised access to personal information being returned by queries, three measures are recommended: (1) to constrain the queries to a known set which don’t specifically ask for personal information, and (2) to limit the individuals and systems which can access the returned information, and (3) to only use relevant and non-personal results in onward processing.